Understanding B2B Market Segmentation: Process and Methods
Business-to-business (B2B) market segmentation is a strategic approach that divides the market into distinct groups of businesses with similar needs or characteristics.
Unlike Business-to-Consumer (B2C) segmentation, B2B segmentation focuses on organizational rather than individual consumers, considering factors such as industry, company size, and purchasing behavior. This extensive guide explores the intricacies of B2B market segmentation, including its importance, process, methods, and practical applications.
Market segmentation is a crucial strategy in both B2B (Business-to-Business) and B2C (Business-to-Consumer) contexts, but its application in the B2B sector requires a nuanced approach.
B2B market segmentation involves dividing a market into distinct groups of businesses that exhibit similar characteristics or needs. This process enables organisations to tailor their marketing efforts, optimise resource allocation, and ultimately drive more effective and efficient business outcomes.
This guide delves into the complexities of B2B market segmentation, detailing the process, methods, and practical applications. By exploring various segmentation criteria and strategies, businesses can better understand how to leverage segmentation to achieve their goals.
Successful B2B marketing strategies rely on well-defined segmentation, ensuring that companies reach the right decision-makers with highly relevant messaging and value propositions. By focusing on precise audience needs, b2b marketing strategies can significantly enhance engagement, drive conversions, and build long-term business partnerships
The Importance of Market Segmentation in B2B
Definition and Purpose
Market segmentation involves partitioning a broad market into smaller, more manageable groups based on shared attributes. In B2B contexts, segmentation is vital for several reasons:
Enhanced Targeting: Segmentation allows businesses to target specific groups more precisely, tailoring their products, services, and marketing messages to meet the unique needs of each segment.
Resource Optimization: By focusing efforts on high-potential segments, companies can allocate resources more efficiently, maximising return on investment. Private equity CRM software supports this process by centralizing deal data and investor insights, helping firms prioritize the most promising opportunities. For instance, in the interior design industry, understanding which segment—like luxury homes or budget-friendly renovations—yields higher returns can significantly enhance resource allocation.
Improved Customer Relationships: Tailored approaches foster stronger relationships with customers by addressing their specific needs and preferences.
Competitive Advantage: A deep understanding of different segments enables businesses to differentiate themselves from competitors and capture niche markets.
Benefits of B2B Market Segmentation
Increased Market Penetration: Tailored marketing strategies lead to better market penetration by resonating with targeted segments.
Effective Product Development: Segmentation insights drive the development of products and services that are closely aligned with the needs of each segment.
Enhanced Sales Efficiency: Sales teams can adopt more effective strategies and approaches when they have a clear understanding of the target segments.
Better Customer Service: Segment-specific approaches lead to enhance customer service by addressing the unique challenges faced by different segments.
The Segmentation Process
Step 1: Define the Market
The first step in the segmentation process is to define the market. This involves a comprehensive understanding of the market's scope and characteristics:
- Market Size and Potential: Assess the overall size of the market and its growth prospects. This involves analysing market reports, industry trends, and economic factors.
- Market Structure: Understand the market structure, including key players, distribution channels, and competitive dynamics.
- Market Needs and Trends: Identify the needs and trends affecting businesses within the market. This includes understanding industry-specific challenges and opportunities.
Step 2: Identify Segmentation Criteria
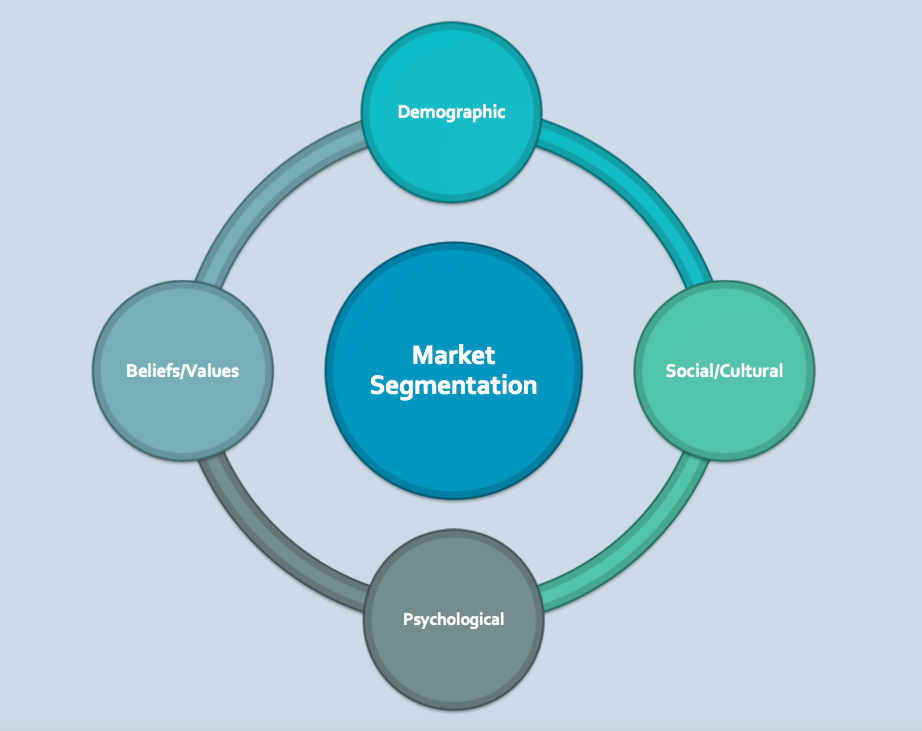
Segmentation criteria are the characteristics used to divide the market into distinct segments. Key criteria include:
Firmographic Criteria:
- Industry: Categorize businesses based on the industry they operate in (e.g., manufacturing, finance, healthcare, event planning). This criterion helps in addressing industry-specific needs.
- Company Size: Segment by company size, often measured by revenue, number of employees, or market share. This helps in tailoring solutions that match the scale of the business.
- Geography: Divide the market based on geographical location (e.g., region, country, city). Geographic segmentation accounts for regional differences in needs and preferences.
Behavioural Criteria:
- Purchasing Behavior: Analyse how businesses make purchasing decisions, including buying frequency, volume, and timing. This helps in targeting businesses with specific purchasing patterns.
- Usage Rate: Segment based on how frequently businesses use a product or service. This includes identifying high-volume users versus occasional users.
- Decision-Making Process: Understand the decision-making process within businesses, including the number of decision-makers and their roles. This helps in developing targeted sales strategies.
Needs-Based Criteria:
- Problem Solving: Identify the specific problems or needs that businesses are trying to address with your products or services. This involves understanding pain points and challenges.
- Benefits Sought: Segment based on the benefits that businesses seek from a product or service. This includes identifying the key benefits that are most valued by each segment.
Psychographic Criteria:
- Company Culture: Understand the culture and values of the target businesses. This includes considering factors such as organisational values and business philosophy.
- Business Objectives: Segment based on the strategic objectives and goals of the businesses. This involves understanding the long-term goals and priorities of each segment.
Technographic Criteria:
- Technology Usage: Segment based on the technology stack and tools that businesses use, including their specific needs and technological environment. For example, this may involve identifying businesses that utilize a heat pump system in their operations.
- Digital Behavior: Analyse online behaviour, including website visits, social media activity, and digital engagement. This helps in tailoring digital marketing strategies to enhance effectiveness and reach, positioning your brand with the best digital marketing agency for optimal results.
Step 3: Collect and Analyze Data
Effective segmentation relies on accurate and comprehensive data. The data collection and analysis process includes:
- Data Collection Methods: Utilise various methods to gather data, including surveys, interviews, industry reports, and company records. Each method has its strengths and limitations.
- Data Analysis: Analyse the collected data to identify patterns and trends. This involves using statistical tools and software to process and interpret data.
Step 4: Develop Segmentation Profiles
Develop detailed profiles for each segment based on the data analysis. These profiles should include:
- Segment Description: A comprehensive description of the segment’s characteristics, needs, and preferences.
- Segment Size and Potential: An assessment of the segment's size and growth potential. This includes estimating the market potential and revenue opportunities.
- Key Challenges and Opportunities: Identify the primary challenges faced by the segment and potential opportunities for the business.
Step 5: Evaluate and Select Target Segments
Evaluate the attractiveness of each segment based on specific criteria:
- Segment Size and Growth Potential: Assess the size of the segment and its potential for growth. Larger and rapidly growing segments may offer more opportunities.
- Segment Profitability: Evaluate the potential profitability of the segment. This includes analysing the revenue potential and cost considerations.
- Competitive Position: Analyse the level of competition within the segment and the business’s ability to compete effectively. This includes understanding competitive dynamics and market positioning.
Based on this evaluation, select the most attractive segments to target. This decision should align with the company’s strategic goals and resources.
Step 6: Develop and Implement Marketing Strategies
With target segments identified, develop and implement marketing strategies tailored to each segment:
- Positioning: Craft a unique value proposition for each segment that addresses their specific needs and preferences. This involves defining how the product or service will be positioned in the market.
- Marketing Mix: Design the marketing mix (product, price, place, promotion) to align with the needs of each segment, leveraging insights from marketing mix modeling to optimize strategy decisions. This includes developing tailored product features, pricing strategies, distribution channels, and promotional tactics.
- Communication Strategies: Develop communication strategies that effectively reach and engage each segment. This includes choosing appropriate communication channels and crafting targeted messages.
Step 7: Monitor and Adjust
Continuously monitor and adjust segmentation strategies based on performance and feedback:
- Performance Tracking: Monitor the effectiveness of marketing strategies and campaigns. This involves analysing key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics.
- Feedback Collection: Gather feedback from customers and stakeholders to identify areas for improvement. This includes conducting surveys, interviews, and analysing customer feedback.
- Adjustments: Make necessary adjustments to segmentation strategies based on performance data and feedback. This ensures that strategies remain relevant and effective.
Methods of B2B Market Segmentation
Firmographic Segmentation
Firmographic segmentation categorises businesses based on firm characteristics. This method involves:
-Industry: Segmenting by industry helps in targeting industry-specific needs and challenges. For example, a software provider may develop different solutions for a mental health practice versus finance.
- Company Size: Segmenting by company size allows businesses to tailor their solutions to match the scale of the business. This includes offering different product tiers or service levels based on company size.
- Geographic Location: Geographic segmentation accounts for regional differences in needs and preferences. This can include local regulations, market conditions, and cultural factors.
Behavioural Segmentation
Behavioural segmentation focuses on the behaviour of businesses in relation to products or services. Key aspects include:
- Purchasing Behaviour: Analysing how businesses make purchasing decisions helps in targeting specific purchasing patterns. This includes identifying frequent buyers versus occasional buyers.
- Usage Rate: Segmenting based on usage rate helps in understanding how frequently businesses use a product or service. High-usage segments may require more customised solutions.
- Decision-Making Process: Understanding the decision-making process within businesses helps in developing targeted sales strategies. This includes identifying key decision-makers and their roles.
Needs-Based Segmentation
Needs-based segmentation divides the market based on the specific needs and problems that businesses are trying to address:
- Problem Solving: Identifying the problems businesses face allows for the development of solutions that address those specific issues. This includes understanding pain points and challenges.
- Benefits Sought: Segmenting based on benefits sought helps in aligning product features with the benefits that businesses value most. This includes identifying the key benefits that resonate with each segment.
Psychographic Segmentation
Psychographic segmentation involves understanding the psychological and cultural factors influencing business behaviour:
- Company Culture: Segmenting based on company culture helps in aligning marketing messages with the values and beliefs of the target businesses. This includes considering factors such as organisational values and business philosophy.
- Business Objectives: Understanding the strategic goals and objectives of businesses allows for the development of solutions that align with their long-term priorities. This includes segmenting based on growth aspirations, market expansion, and innovation goals.
Technographic Segmentation
Technographic segmentation focuses on the technology stack and digital behaviour of businesses:
- Technology Usage: Segmenting based on technology usage helps in understanding the technological environment of different businesses. This includes analysing the tools and platforms they use.
- Digital Behavior: Analysing digital behaviour provides insights into online engagement patterns, including website visits, social media activity, and digital interactions. This helps in tailoring digital marketing strategies.
For example, companies like Swarovski, which may target businesses in the luxury retail sector, could segment their market based on the specific digital tools and platforms these businesses use to enhance customer experience and streamline operations. By understanding the technological environment of these segments, Swarovski can tailor its digital marketing strategies and product offerings to better align with the needs and preferences of its target audience.
Case Studies and Examples
Case Study 1: Technology Solutions Provider
A technology solutions provider used firmographic segmentation to target large enterprises in the finance and healthcare sectors. By developing tailored solutions for these industries, the company increased its market share and achieved higher customer satisfaction. The firm focused on industry-specific needs, such as regulatory compliance in healthcare and data security in finance.
Case Study 2: Manufacturing Equipment Supplier
A manufacturing equipment supplier employed behavioural segmentation to target businesses based on purchasing behaviour and usage rate. By identifying high-volume purchasers and offering customised solutions, the company enhanced its market presence and improved customer loyalty. The firm developed different product tiers and service levels based on usage patterns.
Case Study 3: Business Services Firm
A business services firm utilised needs-based segmentation to address unique challenges faced by different segments. By developing tailored service packages and solutions, the firm successfully increased its client base and achieved higher retention rates. The firm focused on addressing specific problems and delivering targeted benefits to each segment.
Challenges in B2B Market Segmentation
Data Availability and Quality
Obtaining accurate and comprehensive data is a significant challenge in B2B market segmentation. Businesses often face difficulties in accessing reliable data sources and ensuring data quality. Addressing these challenges requires:
- Investing in Data Sources: Investing in high-quality data sources, such as industry reports, market research, and customer databases.
- Ensuring Data Accuracy: Implementing data validation processes to ensure the accuracy and reliability of collected data.
Complexity of Decision-Making
The decision-making process in B2B markets can be complex, involving multiple stakeholders with varying needs and preferences. Navigating financial decisions, such as identifying the right funding options, adds another layer of complexity, and engaging with debt advisory services can help businesses streamline these processes effectively.
This complexity can make it challenging to segment the market effectively. Addressing this challenge involves:
- Understanding Decision-Making Structures: Gaining a clear understanding of the decision-making structures within target businesses, including key decision-makers and their roles.
- Tailoring Approaches: Developing tailored approaches that address the needs and preferences of different stakeholders within the decision-making process.
Dynamic Market Conditions
B2B markets are often subject to dynamic conditions, including changes in technology, regulations, and competitive landscapes. Businesses must continuously adapt their segmentation strategies to respond to these changes. Addressing this challenge involves:
- Monitoring Market Trends: Regularly monitoring market trends and conditions to stay informed about changes affecting the market.
- Adjusting Strategies: Making necessary adjustments to segmentation strategies based on evolving market conditions and emerging opportunities.
Integration with Other Marketing Strategies
Effective market segmentation requires integration with other marketing strategies, including product development, sales, and communication. Ensuring alignment across different functions can be challenging. Addressing this challenge involves:
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Promoting collaboration between different departments, such as marketing, sales, and product development, to ensure alignment and consistency.
- Integrated Strategies: Developing integrated marketing strategies that align segmentation insights with product development, sales approaches, and communication efforts.
Conclusion
B2B market segmentation is a vital strategy that enables businesses to target specific groups within a market more effectively. By understanding and implementing the segmentation process and methods, businesses can optimise their marketing efforts, allocate resources more efficiently, and build stronger relationships with their customers.
The process involves defining the market, identifying segmentation criteria, collecting and analysing data, developing segmentation profiles, evaluating and selecting target segments, and implementing and monitoring marketing strategies.
Different methods of segmentation, including firmographic, behavioural, needs-based, psychographic, and technographic criteria, provide various approaches to understanding and targeting distinct business segments. Each method offers unique insights that can help businesses tailor their offerings and strategies to meet the specific needs of different segments.
However, businesses must navigate challenges such as data availability, decision-making complexity, dynamic market conditions, and integration with other marketing strategies. By addressing these challenges effectively, businesses can leverage segmentation to gain a competitive advantage, enhance market penetration, and achieve their strategic objectives.
In summary, B2B market segmentation is a powerful tool that, when executed thoughtfully, can drive significant business growth and success. By continually refining segmentation strategies and adapting to changing market conditions, businesses can stay ahead of the competition and deliver exceptional value to their target customers.